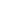
Rectangular tube (RHS) is a hollow square cross-section lightweight thin-walled steel tube, also known as steel cold-formed profile, which is a common pipe material. It is a square section steel with a square cross-section shape and size made of Q235 (A36) hot-rolled or cold-rolled strip or coil as the base material, cold bending and high-frequency welding. It is widely used in construction, machinery manufacturing, automobile manufacturing and other fields. The manufacturing process and technology of rectangular tubes are crucial to guarantee their quality and performance. The most common material is ASTM A500.

2. According to the welding seam - straight seam welded rectangular tube, spiral welded rectangular tube.
The manufacturing processes and technologies for rectangular tubes encompass two main categories: seamless and welded. These involve various forming, welding, and post-processing methods to meet the performance requirements of different applications.
Seamless rectangular tubes are produced by piercing solid round steel bars and then processing them through hot rolling or cold drawing, resulting in a seamless structure. Welded (ERW) rectangular tubes, on the other hand, are made by cold-bending or hot-bending steel plates or strips before welding.
The manufacturing process of rectangular tubes mainly includes: raw material preparation, hot or cold rolling, welding, straightening, cutting and surface treatment.
The manufacturing process and technology of rectangular tubes are the key to ensuring their quality and performance. Through reasonable selection of raw materials, adoption of appropriate rolling and welding processes, straightening, cutting and surface treatment, rectangular tubes of excellent quality can be manufactured to meet various usage requirements.
Key Techniques for Rectangular Tube Production:
1. Rectangular tube forming technology is divided into hot rolling and cold rolling.
Hot rolling is carried out at high temperatures (typically >1000°C), offering high production efficiency but lower dimensional accuracy; it can produce thick-walled, large-section tubes; the material has a uniform microstructure, excellent toughness and ductility; and low residual stress.
Cold rolling (cold bending) is carried out at room temperature, continuously bending the tube into the desired shape through a series of forming rolls, followed by welding, achieving higher precision and surface quality. It offers extremely high production efficiency, great flexibility (easy specification change); and low cost.
2. For seamless tubes, cold drawing further improves dimensional accuracy and surface finish through die drawing; in welding technology, automated welding (such as laser welding) reduces human error, and weld inspection ensures reliability.
3. Surface treatment technologies include pickling, passivation, and galvanizing to enhance weather resistance and aesthetics.
4. Heat treatment processes (such as annealing and quenching) can improve the metal's microstructure and mechanical properties, such as adjusting material hardness and toughness.

Galvanizing: Hot-dip galvanizing provides long-lasting cathodic protection; electro-galvanizing offers a better appearance but weaker protection.
Coating: Spraying with organic coatings such as epoxy and polyester provides physical insulation and aesthetic appeal.
Galvanizing + Coating Composite System: The highest level of corrosion protection.
Quality Control and Development Trends:
Quality control is integrated throughout the entire production process, including raw material composition testing, dimensional tolerance control, non-destructive testing of welds, corrosion protection layer inspection, and final product performance testing.
Development Trends:
High Performance: Application of higher-strength steel grades (such as S700 and S960) and supporting forming and welding technologies.
Green Manufacturing: Energy-saving process optimization and environmentally friendly surface treatment technologies.
Intelligent Production: A full-process intelligent monitoring and quality traceability system based on the Internet of Things and big data.
Application Field of Rectangular Tubes:
1. Building and Structural Engineering
This is the area with the largest consumption of rectangular steel pipes, mainly utilized for their efficient load-bearing capacity in beams, columns, and trusses.
Commercial and Public Buildings:
Main Frame: Steel columns and beams for high-rise office buildings, shopping malls, stadiums, and airport terminals.
Curtain Wall Skeleton System: Serving as the invisible framework supporting glass, stone, and other curtain walls, requiring high precision and corrosion resistance.
Roof Trusses and Space Frames: Used for large-span spatial structures, such as stadium roofs and railway station canopies.
Industrial Buildings:
Factory Structures: Columns, crane beams, and roof trusses for heavy industrial plants.
Equipment Platforms and Pipe Supports: Operating platforms and pipe racks in chemical plants and power plants.
Residential Buildings:
Steel Structure Housing: Serving as load-bearing components in beam-column systems, enabling rapid assembly.
Staircases, Balconies, and Canopies: Railings, handrails, and supporting structures.
2. Transportation Equipment
Primarily utilizing its lightweight and high-strength characteristics as a load-bearing framework.
Automotive Industry:
Commercial Vehicles: Truck chassis beams and cargo box frames are among the most classic applications of rectangular steel tubing.
Buses and Public Transport: Body frames and underframe beams. Special Vehicles: Support structures for fire trucks, RVs, and tank trucks.
New Energy Vehicles: Battery pack housing frames, body anti-collision structural components.
Railways and Rail Transit:
Subways, High-Speed Rail, Trains: Car body underframe, side wall frame, roof curved beams.
Railway Facilities: Platform canopies, overhead contact line supports.
Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering:
Small and Medium-Sized Ships: Hull ribs, deck beams.
Port Machinery: Crane booms, portal frames.
3. Machinery Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
Mainly used as equipment frames, guide rails, and supports, requiring high rigidity and precision.
Machine Tools and Automation Equipment: CNC machine tool beds, robot bases, conveyor line supports.
Agricultural Machinery: Tractor and harvester cab frames and frames.
Mining and Construction Machinery: Excavator and loader booms.
Printing, Textile, and Food Machinery: Shells and internal support structures for various equipment.
4. Infrastructure and Public Facilities
Utilizing its durability and ease of molding, it is used in structures for long-term outdoor use.
Bridge Engineering: Main structures of pedestrian overpasses and landscape bridges; railings and maintenance access for large bridges.
Power and Telecommunications: Transmission towers, communication base station towers, streetlight poles.
Municipal Facilities: Bus stops, guardrails, noise barriers, signposts.
5. Warehousing, Logistics, and Display
Primarily utilizing its ease of assembly and high load-bearing capacity.
Warehousing Systems: Beams and columns for heavy-duty racks (a significant application of rectangular steel tubing).
Logistics Equipment: Forklift forklifts, container frames.
Commercial Display: Shopping mall display cases, display stands, stage trusses.
6. Furniture and Home Decor
Primarily utilizing its modern aesthetics and ease of processing.
Office and Residential Furniture: Tables, chairs, bookshelves, bed frame frames.
Interior and Exterior Decoration: Stair railings, security windows, sunroom frames, railings.
7. Emerging and Specialized Applications
Solar Photovoltaics: The support system for photovoltaic power plants requires corrosion resistance and wind load resistance, making extensive use of galvanized rectangular pipes.
Modular Buildings: Serving as the load-bearing framework for container houses and modular units, enabling rapid construction.
Read more: Material Selection for Square and Rectangular Tubes or Rectangular Tube Sizes Chart
Related information